Rayners walking track
Mount Jerusalem National Park
Overview
Rayners walking track is a family-friendly way to explore Jerusalem National Park, near Mullumbimby. Enjoy beautiful scribbly gum forest as you stroll past pretty streams to the waters of Rayners Dam.
- Where
- Mount Jerusalem National Park in North Coast
- Accessibility
- No wheelchair access
- Distance
- 3.2km return
- Time suggested
- 1hr - 1hr 30min
- Grade
- Grade 2
- What to
bring - Drinking water, sturdy shoes, hat, raincoat, suitable clothing, clothes for all weather conditions, first aid kit, sunscreen, snacks
- Please note
There is no drinking water available in Mount Jerusalem National Park so make sure to bring your own.
An easy 3.2km (1.5 hour) return stroll, Rayners walking track is a great way to introduce children to the beauty of the Koonyum Range. Starting from Koonyum Range Road, you'll soon find yourself walking in dappled sunlight beneath an open canopy of scribbly gums and hairpin banksia trees.
After about 1.6km you'll reach the waters of Rayners Dam which has amazing reflections from the the tea tree stained waters. As you walk, keep an eye out for the park's diverse wildlife, especially near the 3 stream crossings. Yellow-tailed black cockatoos, satin bowerbirds and koalas are just some of the animals that make their homes here. You might even spot a wedge tailed eagle soaring overhead.
Spring and autumn are great times to visit, as wildflowers bloom and add patches of colour throughout the forest. And at dusk you can glimpse long-nosed bandicoots, sugar gliders and southern boobook owls.
If this taste of bushwalking in the Byron Bay hinterland whets your appetite, try child-friendly Boggy Creek walk in Whian Whian State Conservation Area, or the longer Minyon Falls walking track in Nightcap National Park.
Also see
-

Boggy Creek walk
Boggy Creek walk in Whian Whian State Conservation Area takes you through blackbutt forest and along the beautiful Boggy Creek to Minyon Falls. You can swim in the inviting pools along the creek.
-

Minyon Falls walking track
Popular with visitors to the Byron Bay area, Minyon Falls walking track leads through rainforest to a scenic waterfall in Nightcap National Park, in northern NSW.
Map
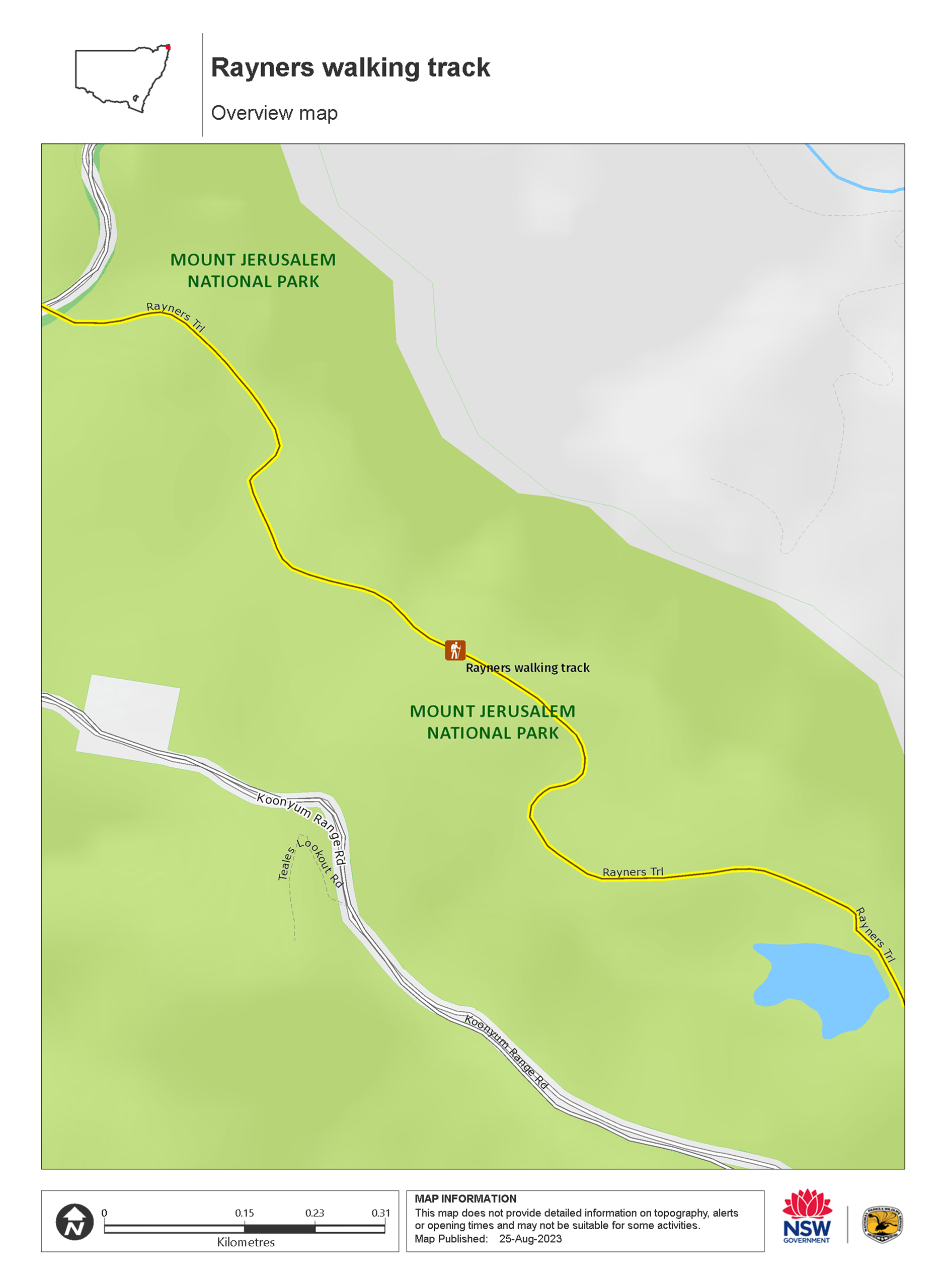
Map legend

Local alerts
For the latest updates on fires, closures and other alerts in this area, see https://www.nationalparks.nsw.gov.au/things-to-do/walking-tracks/rayners-walking-track/local-alerts
General enquiries
- National Parks Contact Centre
- 7am to 7pm daily
- 1300 072 757 (13000 PARKS) for the cost of a local call within Australia excluding mobiles
- parks.info@environment.nsw.gov.au
Park info
- in Mount Jerusalem National Park in the North Coast region
Mount Jerusalem National Park is always open but may have to close at times due to poor weather or fire danger.
Visitor info
All the practical information you need to know about Rayners walking track.
Track grading
Features of this track
Distance
3.2km return
Time
1hr - 1hr 30min
Quality of markings
Clearly sign posted
Experience required
No experience required
Gradient
Gentle hills
Steps
No steps
Quality of path
Formed track
Getting there and parking
Rayners walking track is in the Koonyum Range area of Mount Jerusalem National Park.
To get there from Mullumbimby:
- Drive south on Jubilee Avenue.
- Continue straight on Coolamon Scenic Drive for about 1 km.
- Turn right onto Wilsons Creek Road and drive for 5.1km.
- Turn right onto Koonyum Range Road and drive for 2.6km.
- After entering the park, continue on Koonyum Range Road for a further 2.3km.
- Rayners walking track trailhead is on your right.
Road quality
Koonyum Range Road is a dry weather road. Driving this road after heavy rain is not recommended.
- Mixture of sealed and unsealed roads
Vehicle access
- Most roads suitable for 2WD vehicles
Weather restrictions
- Dry weather only
Parking
Limited parking is available on the side of Koonyum Range Road.
Best times to visit
Autumn
Autumn's a great time to visit as you escape the heat of summer and avoid the chill of winter.
Spring
If you're interested in wildflowers, visit in spring to see them bloom and add patches of colour throughout the forest.
Facilities
- There are no bins so you'll need to take all rubbish away with you.
- Be sure to bring your own drinking water because none is available in Mount Jerusalem National park.
Maps and downloads
Accessibility
Disability access level - no wheelchair access
Permitted
Cycling
Mountain biking is permitted on this track and some nearby management trails.
Prohibited
Camp fires and solid fuel burners
Camping
Fishing
Gathering firewood
Generators
Horses
Pets
Pets and domestic animals (other than certified assistance animals) are not permitted. Find out which regional parks allow dog walking and see the pets in parks policy for more information.
Smoking
NSW national parks are no smoking areas.
Learn more
Rayners walking track is in Mount Jerusalem National Park. Here are just some of the reasons why this park is special:
Diverse ecosystems

Mount Jerusalem National Park supports several diverse ecosystems including sub-tropical rainforest. It provides refuge for more than 16 threatened mammal species, 11 threatened bird species, 3 threatened frog species and 20 threatened plant species. Be sure to listen out for the threatened wompoo fruit-dove or the mimicking calls of the Albert’s lyrebird while in the rainforest, as well as the screech of the yellow-tailed black cockatoo high up in the eucalypt canopy. If you’re lucky you could also see a spiky echidna or a red-legged pademelon passing by on the forest floor.
- Gilwah trail With beautiful forests and stunning mountain views, Gilwah trail near Mullumbimby is a great way for horse riders, mountain bikers and bushwalkers to explore Mount Jerusalem National Park.
- Mount Jerusalem Central trails Get off the beaten track on Mount Jerusalem Central trails, near Mullumbimby. These multi-use trails through beautiful eucalypt forest are ideal for horse riders, mountain bikers and bushwalkers.
Volcanic history

Mount Jerusalem National Park forms part of the outer rim of the Tweed Caldera which was an active volcano around 21 million years ago. Millions of years of weathering and erosion have seen the Tweed Shield Volcano form a large valley roughly 1,000m deep and 40km wide, now known as the Tweed Valley. Today Mount Jerusalem National Park forms a range along the south-eastern rim of the Tweed Caldera between the Tweed Valley and Byron Shire, where head waters of the Tweed, Brunswick and Wilsons Rivers can be found.
- Gilwah trail With beautiful forests and stunning mountain views, Gilwah trail near Mullumbimby is a great way for horse riders, mountain bikers and bushwalkers to explore Mount Jerusalem National Park.
- Mount Jerusalem Central trails Get off the beaten track on Mount Jerusalem Central trails, near Mullumbimby. These multi-use trails through beautiful eucalypt forest are ideal for horse riders, mountain bikers and bushwalkers.
Plants and animals protected in this park
Animals
-

Brown-striped frog (Lymnastes peronii)
One of the most common frogs found in Australia, the ground-dwelling brown-striped frog lives in ponds, dams and swamps along the east coast. Also known as the striped marsh frog, this amphibian grows to 6.5cm across and has a distinctive ‘tok’ call that can be heard all year round.
-

Common brushtail possum (Trichosurus vulpecula)
One of the most widespread of Australian tree-dwelling marsupials, the common brushtail possum is found across most of NSW in woodlands, rainforests and urban areas. With strong claws, a prehensile tail and opposable digits, these native Australian animals are well-adapted for life amongst the trees.
-

Common ringtail possum (Pseudocheirus peregrinus)
Commonly found in forests, woodlands and leafy gardens across eastern NSW, the Australian ringtail possum is a tree-dwelling marsupial. With a powerful tail perfectly adapted to grasp objects, it forages in trees for eucalypt leaves, flowers and fruit.
-

Eastern bentwing-bat (Miniopterus schreibersii oceanensis)
Eastern bentwing-bats congregate in caves across the east and north-west coasts of Australia, in colonies of up to 150,000. These small Australian animals weigh around 13-17g and can reach speeds of up to 50km per hour. Eastern bentwing-bats use both sight and echolocation to catch small insects mid-air.
-

Eastern blue-tongue lizard (Tiliqua scinciodes)
The eastern blue-tongue lizard, one of the largest skinks in Australia, is found throughout most of NSW. When threatened, the eastern blue-tongue lizard displays its blue tongue in a wide-mouthed intimidating show. Not an agile animal, they feed on slow-moving beetles and snails.
-

Eastern water dragon (Intellagama lesueurii lesueurii)
The eastern water dragon is a subaquatic lizard found in healthy waterways along eastern NSW, from Nowra to halfway up the Cape York Pensinsula. It’s believed to be one of the oldest of Australian reptiles, remaining virtually unchanged for over 20 million years.
-

Koala (Phascolarctos cinereus)
One of the most renowned Australian animals, the tree-dwelling marsupial koala can be found in gum tree forests and woodlands across eastern NSW, Victoria and Queensland, as well as in isolated regions in South Australia. With a vice-like grip, this perhaps most iconic but endangered Australian animal lives in tall eucalypts within a home range of several hectares.
-

Kookaburra (Dacelo novaeguineae)
Of the 2 species of kookaburra found in Australia, the laughing kookaburra is the best-known and the largest of the native kingfishers. With its distinctive riotous call, the laughing kookaburra is commonly heard in open woodlands and forests throughout NSW national parks, making these ideal spots for bird watching.
-

Lace monitor (Varanus varius)
One of Australia’s largest lizards, the carnivorous tree-dwelling lace monitor, or tree goanna, can grow to 2m in length and is found in forests and coastal tablelands across eastern Australia. These Australian animals are typically dark blue in colour with whitish spots or blotches.
-

Long-nosed bandicoot (Perameles nasuta)
A nocturnal marsupial and one of the smaller Australian native animals, the long-nosed bandicoot is found across eastern Australia. Populations in the Sydney region have dwindled since European settlement, leaving only endangered colonies in inner western Sydney and at North Head, near Manly. The long-nosed bandicoot has grey-brown fur and a pointed snout which it uses to forage for worms and insects.
-

Peron's tree frog (Litoria peroni)
Peron’s tree frog is found right across NSW. These tree-climbing and ground-dwelling Australian animals can quickly change colour, ranging from pale green-grey by day, to a reddish brown with emerald green flecks at night. The male frog has a drill-like call, which has been described as a 'maniacal cackle’.
-

Satin bowerbird (Ptilonorhynchus violaceus)
With vibrant blue-violet eyes and curious antics, the satin bowerbird is a favourite for bird watching and easy to spot as it forages for food in open forest. Relatively common across eastern Australia, in NSW they’re found in coastal rainforests and adjacent woodlands and mountain ranges.
-

Short-beaked echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus)
One of only 2 egg-laying mammals in the world, the short-beaked echidna is one of the most widespread of Australian native animals. Covered in spines, or quills, they’re equipped with a keen sense of smell and a tube-like snout which they use to break apart termite mounds in search of ants.
-

Southern boobook (Ninox novaeseelandiae)
The southern boobook, also known as the mopoke, is the smallest and most common native owl in Australia. With a musical 'boo-book' call that echoes through forests and woodlands, the southern boobook is a great one to look out for while bird watching.
-

Sugar glider (Petaurus breviceps)
The sugar glider is a tree-dwelling Australian native marsupial, found in tall eucalypt forests and woodlands along eastern NSW. The nocturnal sugar glider feeds on insects and birds, and satisfies its sweet tooth with nectar and pollens.
-

Superb lyrebird (Menura novaehollandiae)
With a complex mimicking call and an elaborate courtship dance to match, the superb lyrebird is one of the most spectacular Australian animals. A bird watching must-see, the superb lyrebird can be found in rainforests and wet woodlands across eastern NSW and Victoria.
-

Swamp wallaby (Wallabia bicolor)
The swamp wallaby, also known as the black wallaby or black pademelon, lives in the dense understorey of rainforests, woodlands and dry sclerophyll forest along eastern Australia. This unique Australian macropod has a dark black-grey coat with a distinctive light-coloured cheek stripe.
-

Tawny frogmouth (Podargus strigoides)
Found throughout Australia, the tawny frogmouth is often mistaken for an owl due to its wide, powerful beak, large head and nocturnal hunting habits. The ‘oom oom oom’ call of this native bird can be heard echoing throughout a range of habitats including heath, woodlands and urban areas.
-

Wedge-tailed eagle (Aquila audax)
With a wingspan of up to 2.5m, the wedge-tailed eagle is Australia’s largest bird of prey. These Australian animals are found in woodlands across NSW, and have the ability to soar to heights of over 2km. If you’re bird watching, look out for the distinctive diamond-shaped tail of the eagle.
-

Yellow-tailed black cockatoo (Calyptorhynchus funereus)
The yellow-tailed black cockatoo is one of the largest species of parrot. With dusty-black plumage, they have a yellow tail and cheek patch. They’re easily spotted while bird watching, as they feed on seeds in native forests and pine plantations.
-

Albert's lyrebird (Menura alberti)
The Albert’s lyrebird is much rarer than the superb lyrebird. Distinguished by its richer brown plumage and less elaborate tail feathers, it’s protected as a threatened species in NSW.
Plants
-

Blueberry ash (Elaeocarpus reticulatus)
The blueberry ash is a rainforest shrub which produces blue olive-shaped berries and spectacular bell-shaped flowers, which often appear on the plant together. It is a tall slender shrub or small tree found in rainforest, tall eucalypt forest and coastal bushland in eastern NSW, south-east Queensland and Victoria.
-

Coachwood (Ceratopetalum apetalum)
Coachwood trees are Australian native plants that grow in warm temperate rainforests along coastal NSW. Also known as scented satinwood, the mottled grey bark of the coachwood has horizontal markings and a delicate fragrance.
-

Grass tree (Xanthorrea spp.)
An iconic part of the Australian landscape, the grass tree is widespread across eastern NSW. These Australian native plants have a thick fire-blackened trunk and long spiked leaves. They are found in heath and open forests across eastern NSW. The grass tree grows 1-5m in height and produces striking white-flowered spikes which grow up to 1m long.
-

Scribbly gum (Eucalyptus haemastoma)
Easily identifiable Australian native plants, scribbly gum trees are found throughout NSW coastal plains and hills in the Sydney region. The most distinctive features of this eucalypt are the ‘scribbles’ made by moth larva as it tunnels between the layers of bark.
-

Wonga wonga vine (Pandorea pandorana)
The wonga wonga vine is a widespread vigorous climber usually found along eastern Australia. A variation of the plant occurs in the central desert, where it resembles a sprawling shrub. One of the more common Australian native plants, the wonga wonga vine produces bell-shaped white or yellow flowers in the spring, followed by a large oblong-shaped seed pod.

